ARTS是
由左耳朵耗子--陈皓发起的一个活动: 每周至少做一个leetcode的算法题、阅读并点评至少一篇英文技术文章、学习至少一个技术技巧、分享一篇有观点和思考的文章。(也就是Algorithm、Review、Tip、Share简称ARTS),至少坚持一年。
ARTS 018
这是第18篇
Algorihm 算法题
107. 二叉树的层次遍历 II(Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II)
题目难度: 简单
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其自底向上的层次遍历为:
[
[15,7],
[9,20],
[3]
]
Solution
Language: C
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *columnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int** levelOrderBottom(struct TreeNode* root, int** columnSizes, int* returnSize) {
}
/**
- Definition for a binary tree node.
- struct TreeNode {
- int val;
- struct TreeNode *left;
- struct TreeNode *right;
- }; */ /**
- Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
- The sizes of the arrays are returned as *columnSizes array.
- Note: Both returned array and columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode root, int** columnSizes, int* returnSize) {
}
方法1
int getLevelOrderBottom(struct TreeNode* root, int*** ArrayRet, int** columnSizes, int length, int level) {
if (root == NULL) return length;
int size = length;
if (level>size - 1) {
*ArrayRet = realloc(*ArrayRet, sizeof(int*)*(size + 1));
(*ArrayRet)[level]= calloc(0, sizeof(int));
*columnSizes = realloc(*columnSizes, sizeof(int)*(size + 1));
(*columnSizes)[level] = 0;
size++;
}
(*ArrayRet)[level] = realloc((*ArrayRet)[level], sizeof(int)*((*columnSizes)[level] + 1));
(*ArrayRet)[level][(*columnSizes)[level]] = root->val;
(*columnSizes)[level] += 1;
size = getLevelOrderBottom(root->left, ArrayRet, columnSizes, size, level + 1);
size = getLevelOrderBottom(root->right, ArrayRet, columnSizes, size, level + 1);
return size;
}
int** levelOrderBottom(struct TreeNode* root, int** columnSizes, int* returnSize) {
int **ArrayRet = calloc(0, sizeof(int *));
*returnSize = getLevelOrderBottom(root, &ArrayRet, columnSizes, 0, 0);
//reverse the array
int **ret = calloc(*returnSize, sizeof(int *));
for(int i=0;i<*returnSize;i++){
ret[i]=calloc((* columnSizes)[*returnSize-i-1],sizeof(int));
memcpy(ret[i],ArrayRet[*returnSize-i-1],sizeof(int)*(* columnSizes)[*returnSize-i-1]);
}
int k=0,j=* returnSize-1;
while(k<j){
int tmp=(* columnSizes)[k];
(* columnSizes)[k++]=(* columnSizes)[j];
(* columnSizes)[j--]=tmp;
}
return ret;
}
方法2,来自LeetCode提交记录:
int GetdepthofTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if (!root) return 0;
int left = GetdepthofTree(root->left);
int right = GetdepthofTree(root->right);
if (left > right)
return left+1;
else
return right+1;
}
int** levelOrderBottom(struct TreeNode* root, int** columnSizes, int* returnSize) {
if (!root){
return NULL;
}
//获取二叉树的深度,最大层数或者说
int depth = *returnSize = GetdepthofTree(root);
//ret是一个指向一个二维数组的指针,这一块地址是我们自己开辟的,需要malloc
int** ret = (int**)malloc(depth*sizeof(int*));
//columnSizes是一个指向指针的指针,这个地址已经指定了,就是说这个地址了存放的下一个地址已经确定了,但是下一个地址里存放的还是地址,这个地址任然不确定,那么就需要malloc了
//*columnSizes是一个指向一个一维数组的指针,数组的大小也是depth
*columnSizes = (int*)malloc(depth*sizeof(int));
int front = 0, back = 0;
struct TreeNode* queue[10000];
queue[back++] = root;
while (front < back){
int start = front, end = back;
(*columnSizes)[--depth] = end - start;
front = end;
//开始的时候我们只给了ret的地址,因为ret是一个二维数组的起始地址,但是这个二维数组里面的一维数组的地址并没有确定,就需要malloc来确定
ret[depth] = (int*)malloc((end - start)*sizeof(int));
for (int i=start; i<end; i++){
ret[depth][i-start] = queue[i]->val;
if (queue[i]->left) queue[back++] = queue[i]->left;
if (queue[i]->right) queue[back++] = queue[i]->right;
}
}
return ret;
}
Review
参见: 常见的数据结构与算法: https://dandan2009.github.io/2018/11/28/data-structures-part3-language-support/
TIPS
A Beginner’s Guide to Coding Graphics Shaders.
https://gamedevelopment.tutsplus.com/series/a-beginners-guide-to-coding-graphics-shaders–cms-834
这个系列还不错。 可以作为 Graphics Shaders 入门教程看看。
iOS模拟弱网方法:
- 使用真机,真机在设置里面有个开发中选项,有个 Network Link Conditioner的选项,
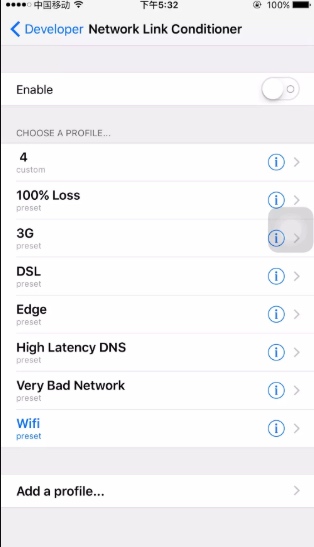 选择其中一种类型的网络,可以设置网络速率
选择其中一种类型的网络,可以设置网络速率
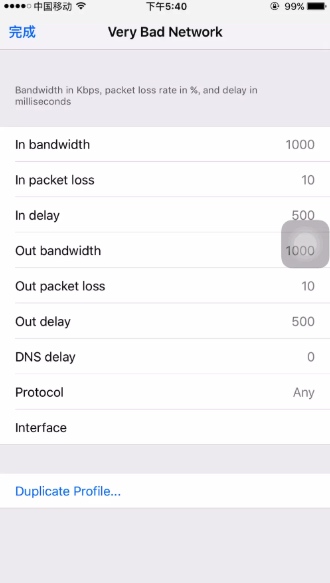
-
模拟器设置弱网环境: 方法1 :到Apple开发者中心下载Additional Tools for Xcode
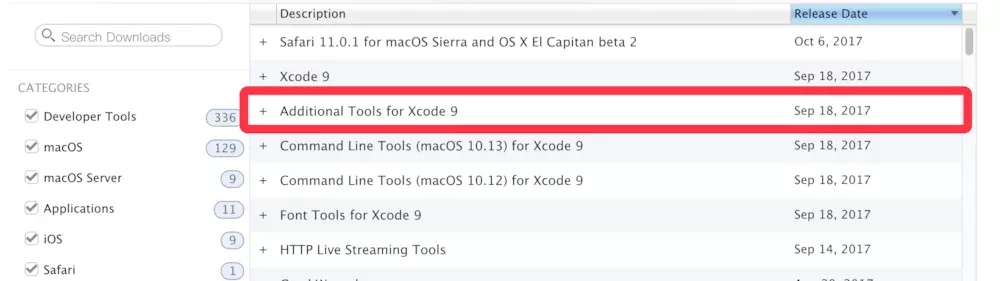
 打开系统偏好设置,找到Network Link Conditioner,双击打开。
打开系统偏好设置,找到Network Link Conditioner,双击打开。
Network Link Conditioners是对整个系统有效的,普通上网的速度也会被限制, 所以在测试完毕时,记得停止Network Link Conditioner .
方法2:Charles
Share
分界几个算法的可视化学习工具和网站:
旧金山大学数据结构和算法 http://hao.jobbole.com/visualizing-algorithms-and-data-structure/
VisuAlgo:通过动画学习算法和数据结构 http://hao.jobbole.com/visualgo/
Algomation:查看、创建和分享算法的学习平台 http://hao.jobbole.com/algomation/
Algorithm Visualizer:
http://algorithm-visualizer.org
Algorithm Visualizer 在 GitHub 有 10.6k+ Star:
https://github.com/algorithm-visualizer/algorithm-visualizer
分享一个英文学习的网站:https://learnamericanenglishonline.com/Red%20Level/R1%20Do.html