Data Structures — Diving Into Data Structures (Part 1) 数据结构-深入到数据结构(第1部分)
文章来源:https://medium.com/omarelgabrys-blog/diving-into-data-structures-6bc71b2e8f92
[TOC]
When we have a programming problem, we dive into the algorithm, while ignoring the underlying data structure. And even worse, we think that using another data structure won’t make much of a difference, although we could vastly improve the performance of our code by picking an alternative data structure. 当我们遇到编程问题时,我们深入研究算法,同时忽略底层的数据结构。更糟糕的是,我们认为使用另一种数据结构不会有太大的区别,尽管我们可以通过选择另一种数据结构来极大地提高代码的性能。
What Is A Data Structure 什么是数据结构
It doesn’t start without asking: What the heck data structure is? 它不是一开始就问:该死的数据结构是什么?
It’s an intentional arrangement of a collection of data that we’ve built. 是我们构建的数据集合的有意安排。
Intentional Arrangement 故意安排
The intentional arrangement means the arrangement done on purpose to impose, to enforce, some kind of systematic organization on the data. 故意安排是指有目的的安排,目的是对数据进行某种系统的组织。 故意安排是指故意对数据进行某种系统组织的安排。 故意安排是指有意安排,强制执行某种系统的数据组织。
Because it’s useful, it makes our lives easier, and it’s easy to manage when you keep related information together. 因为它是有用的,它使我们的生活更容易,当你把相关的信息放在一起时,它很容易管理。
Data Structures In our Life 我们生活中的数据结构
We need data structures in our programs because we think this way as human beings. 在我们的程序中,我们需要数据结构,因为我们人类就是这样思考的。
A recipe is an actual data structure, as is a shopping list, a telephone directory, a dictionary, etc. They all have a structure, they have a format. 菜谱是一个实际的数据结构,就像购物清单、电话簿、字典等一样。它们都有一个结构,它们都有一个格式。
Data Structure and Object Oriented Programming 数据结构和面向对象编程
Now if you’re an object oriented programmer, you may be thinking, Well isn’t this what we do with classes and objects?. 如果你是一个面向对象的程序员,你可能会想,这难道不是我们对类和对象所做的吗?
I mean, we define these real-world objects in a program because we think this way as human being, or at least we’re supposed to. 我的意思是,我们在一个程序中定义这些真实世界的对象,因为我们以人类的方式思考,或者至少我们应该这样想。
And yes, absolutely. Objects are a type of data structure, and not the only one. 是的,当然。对象是一种数据结构,而不是唯一的一种。
Five Fundamental Behaviors 五种基本行为
How to access, insert, delete, find, & sort. These are the operations that you will most likely going to perform. 如何访问、插入、删除、查找和排序。这些是您最有可能执行的操作。
Not all of data structures have the five fundamental behaviors. 并不是所有的数据结构都有这五种基本行为。
For example, many data structures don’t support any kind of searching behavior, It’s just a big collection, a big container of stuff, and If you need to find something, you just go through all of it yourself. And many don’t provide any kind of sorting behavior. Others are naturally sorted. 例如,许多数据结构不支持任何类型的搜索行为,它只是一个大集合,一个大容器的东西,如果你需要找到什么东西,你只需要自己遍历它。而且很多都不提供任何排序行为。其他的自然排序。
Each data structure has it’s own different way, or different algorithm for sorting, inserting, finding, …etc, Why? Because, due to the nature of the data structure, there are algorithms used with specific data structure, where some other can’t be used. 每个数据结构都有自己不同的方式,或者不同的排序、插入、查找等算法,为什么?因为,由于数据结构的性质,有一些算法与特定的数据结构一起使用,而其他一些算法不能使用。
The more efficient & suitable the algorithm, the more you will have an optimized data structure. These algorithms might be built-in or implemented by developer to manage and run these data structures. 算法越高效、越适用,就越能得到优化的数据结构。这些算法可以是内置的,也可以由开发人员实现来管理和运行这些数据结构。
Always read the language documentation and check the performance of the algorithms used with the underlying data structure. Different algorithms might be used based on the data (it’s size, type, …) you have. 总是阅读语言文档并检查与底层数据结构一起使用的算法的性能。不同的算法可能会基于数据(数据的的大小,类型,…)来使用。
One-Dimensional Arrays 一维数组
The array is the most fundamental, the most commonly used data structure across all programming languages. The support for one-dimensional arrays is generally built directly into the core language itself. 数组是所有编程语言中最基本、最常用的数据结构。对一维数组的支持通常直接构建到核心语言本身中。
An array is an ordered collection of items, where each item inside the array has an index. 数组是有序的项集合,数组中的每个项都有一个索引。
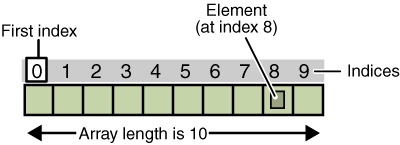
Indexes 索引
The indexes are in order, they are zero-based index in most languages, but, that’s not the case with other few languages. 索引是按顺序排列的,在大多数语言中它们是基于零的索引,但在其他少数语言中并非如此。
Size 尺寸
The simplest arrays are fixed size, also called immutable, meaning unchangeable arrays. They can be created initially at any size. But once the array is created, you can’t add or remove elements from it. 最简单的数组是固定大小的,也称为不可变数组,意思是不能改变的数组。它们最初可以以任何大小创建。但是一旦创建了数组,就不能从其中添加或删除元素。
Sometimes the ability to dynamically add or remove elements from it while the program is running is made available in the standard array in a language, and sometimes you have multiple different array types, depending on whether you need a fixed or resizable array. 有时,在程序运行时动态添加或删除元素的功能可以在语言的标准数组中使用,有时您可以使用多种不同的数组类型,这取决于您需要的是固定的数组还是可调整大小的数组。
Data Type 数据类型
Simple arrays are typically restricted to a specific type of data. It’s an array of integers, or an array of booleans. But some languages allow you to create arrays of just generic objects, meaning you could put different data types. 简单数组通常仅限于特定类型的数据。它是一个整数数组,或者布尔数组。但有些语言允许创建泛型对象的数组,这意味着可以放置不同的数据类型。
array = [123, true, "string", [1,2,3], object]
Multidimensional Arrays 多维数组
Taking the one dimensional array one step further, we can have arrays with two dimensions. 进一步考虑一维数组,我们可以得到二维数组。
It’s basically an array of arrays, where each item in this array itself contains another array. 它本本上是一个数组的数组,数组中的每个项本身都包含另一个数组。
Therefore, any single array element is not accessed with just one index, but we need two numbers to get to it. Sometimes referred to as a matrix or a table because this is, effectively, rows and columns of information. 因此,任何单个数组元素都不能只用一个索引访问,而是需要两个数字才能访问它。有时被称为矩阵或表,因为这实际上是信息的行和列。
We can take the two-dimensional array further to three-dimensional arrays and even more. 我们可以把二维数组进一步发展到三维数组,甚至更多。
Jagged Arrays 交错数组
When we have a Multidimensional array, where each row, each item needs to have different number of items. It’s where Jagged arrays come into play. 当我们有一个多维数组时,每一行,每项都需要有不同数量的项。这就是交错数组发挥作用的地方。
It’s a Multidimensional array where each item can have different sizes. 是一个多维数组,每个条目可以有不同的大小。
 Rows have different number of stones
行有不同数量的石头
Rows have different number of stones
行有不同数量的石头
When To Use Jagged Arrays 何时使用交错数组
If you have a multidimensional array which records the number of sales every day. The first index is for the month, while the second is for the day. 如果你有一个多维数组记录每天的销售额。第一个指数是当月的,第二个指数是当天的。
sales = [[124,153,135, …], [135,545,342,678,], …]
You can notice that Jan has 31 days, while Feb 29, and so on. So, either leaving the irrelevant elements empty, or setting them to 0 or -99 or some other value is not always desirable. But, you shouldn’t have elements that represent impossibilities. Like In February, where days 30 & 31 don’t exist. 你可以注意到一月有31天,而二月29日,等等。因此,将不相关的元素保持为空,或将它们设置为0或-99或其他值并不总是可取的。但是,你不应该有代表不可能的元素。比如在2月份,30天和31天是不存在的。
So, Using Jagged Arrays, we can get the average of sales in a month by grabbing all the sales in that month, add them all, and divide by the number of days in that month, without having to add logic to figure out the days we should be ignoring. 因此,使用交错数组,我们可以得到一个月的平均销售额,通过抓取当月的所有销售额,将它们相加,然后除以当月的天数,而不需要添加逻辑来计算应该忽略的天数。
Resizable Arrays 可调整大小的数组
Most languages provide some kind of resizeable array, or dynamic array, or mutable. In Java, the standard array is fixed-size and a fixed data type, but, you can also create a resizeable array using ArrayList. 大多数语言都提供某种可调整的数组、动态数组或可变数组。在Java中,标准数组是固定大小和固定数据类型的,但是,您也可以使用ArrayList创建可调整大小的数组。
Adding & Removing 添加和删除
The location where we add a new element or remove an existing one does matter, because adding or removing an element at the end is faster than at some where else. 添加新元素或删除现有元素的位置确实很重要,因为在末尾添加或删除元素要比在其他地方快。
So, elements will have to be shifted to the left or to the right, and re-indexed; re-ordered. Therefore, it does have a performance impact. 因此,元素必须向左或向右移动,并重新建立索引;重新定购商品。因此,它确实会对性能产生影响。
The way of shifting, differs from language to another, some will be shifting items in place, but, some other will just copy the entire contents of the old array into a new one with the item being added or removed. 转换的方式,根据语言的不同,有些会在适当的位置移动项,但是,有些只会将旧数组的全部内容复制到一个新数组中,同时添加或删除项。
Sorting Arrays 排序数组
Sorting is always computationally intensive, you might need to do it but we want to minimize it. So, keeping aware about how much data we have and how often we’re asking to sort might lead us into choosing different data structures. 排序总是计算密集型的,你可能需要这样做但我们想最小化它。因此,了解我们有多少数据以及我们要求排序的频率可能会导致我们选择不同的数据结构。
 Sorting people by height —pleacher.com
按高度分类
Sorting people by height —pleacher.com
按高度分类
The Built-In Sorting Functionality 内置的排序功能
When we’re sorting arrays, there are things you need to understand the built-in sort functionality. 当我们对数组进行排序时,您需要了解内置的排序功能。
Second, Is the built-in sort functionality will attempt to sort an existing array in place or will create another copy?. Most languages will attempt to sort an existing array in place, while a few will create new copy of the original array to contain the sorted array. 其次,内置的排序功能是试图对现有数组进行排序,还是创建另一个副本?大多数语言将尝试对现有数组进行排序,而少数语言将创建原始数组的新副本,以包含已排序的数组。
Sorting Custom Objects 排序自定义对象
In object orientated languages, you often have arrays of your own custom objects, not just arrays of simple numeric or even string values. 在面向对象的语言中,您通常拥有自己定制对象的数组,而不仅仅是简单的数字数组甚至字符串数组。
When you then ask that array to sort those objects using the built in sort functionality in the language. It simply won’t know how to do it. Because you need to provide a little more information on which property to sort accordingly. 然后请求该数组使用语言中内置的排序功能对这些对象进行排序。它根本不知道怎么做。因为您需要提供关于相应排序属性的更多信息。
So, for example, sort the users by their id, name, or birth date. This defines the object’s property to sort accordingly. 例如,按用户的id、姓名或出生日期对用户进行排序。这就定义了对象的属性来进行相应的排序。
Usually only needs a few lines and it’s typically called a comparator, or compare function, or compare method. 通常只需要几行代码,通常称为比较器、比较函数或比较方法。
##Searching Arrays 搜索数组
If we wanted to know if a specific value exists somewhere in an array or not, we could loop over array elements, and check the value at that current position, and see if it’s equal to goal or not. 如果我们想知道一个特定的值是否存在于数组中,我们可以循环遍历数组元素,检查当前位置的值,看看它是否等于goal。
 Keep searching even under the bed
即使在床底下也要继续寻找
Keep searching even under the bed
即使在床底下也要继续寻找
The best case scenario is that the first element is the value we’re looking for. The worst case is that the value is at the end or does not appear anywhere in the array. This method is referred to as a linear search or a sequential search. This is an inelegant brute-force method. 最好的情况是,第一个元素是我们正在寻找的值。最坏的情况是值在数组的末尾或不在数组的任何位置出现。这种方法称为线性搜索或顺序搜索。这是一种不雅的蛮力法。
While linear searches are simple to understand and they are easy to write and they will work, but, they’re slow. And the more elements you have, the slower they get. 虽然线性搜索很容易理解,也很容易编写,而且会工作,但是,它们很慢。元素越多,速度越慢。
Data Needs To Be Ordered 需要对数据进行排序
If there is no order, no predictable sequence to the values in the array, then, there may be no other options than check all the array elements. 如果数组中的值没有顺序,没有可预测的序列,那么除了检查所有数组元素之外,可能没有其他选项。
So, data must be ordered in a way so that we can use an algorithm other than linear search. Therefore, having some kind of order to those elements is more and more significant. 因此,数据必须以某种方式排序,这样我们才能使用线性搜索之外的算法。因此,对这些元素进行排序变得越来越重要
The Inherit Challenge of Data Structures 数据结构的继承挑战
You may sometimes agree to use a slow search ability, because the only way of fixing that is to sort the array, which in turn will add a performance hit that it’s simply not worth it. 有时您可能会同意使用慢速搜索功能,因为解决这个问题的唯一方法是对数组进行排序,这反过来又会增加性能损失,这根本不值得。
So, If you are going to search on an array once, It’s better to have a complexity of O(N) for linear search, than O(NLogN) for sorting + O(LogN) for searching. If, however, you are going to search a lot, then, you may first sort the array once at the beginning, and now, you can search with O(LogN) every time instead of linear search O(N). 所以,如果你要在一个数组上搜索一次,对于线性搜索来说O(N)比O(NLogN)排序+ O(LogN)更复杂。但是,如果要进行大量搜索,那么您可以首先在开始时对数组进行一次排序,现在,您可以每次使用O(LogN)搜索,而不是使用线性搜索O(N)。
You cannot have a data structure that is equally good in all situations. A naturally sorted data structure requires less time in searching for an element, and more time in inserting because it keeps the array sorted. While a basic array requires more time in searching, and less time in inserting elements to the end of the array. 你不可能拥有一个在所有情况下都同样优秀的数据结构。自然排序的数据结构需要更少的时间来搜索元素,而插入更多的时间,因为它保持数组的排序。而基本数组需要更多的搜索时间,在数组末尾插入元素的时间更少
##Lists 列表
Lists are pretty simple data structures. It’s structure keeps track of sequence of items. 列表是非常简单的数据结构。它的结构可以跟踪项目的顺序。
It’s a collection of items (called nodes) ordered in a linear sequence.
它是按线性顺序排列的项(称为节点)的集合。
These nodes don’t need to be allocated next to each other in the memory like an array is. 这些节点不需要像数组那样在内存中相邻分配。
There is a general theoretical programming concept of a list, and there is the specific implementation of a list data structure, which may have taken this basic list idea and added a whole bunch of functionality. Lists are implemented either as linked lists (singly, doubly, circular, …) or as dynamic array. 列表有一个一般的理论编程概念,还有一个列表数据结构的具体实现,它可能采用了这个基本的列表概念并添加了一大堆功能。列表既可以实现为链表(单链表、双链表、循环链表、循环链表),也可以实现为动态数组。
An Array Vs A List 数组Vs列表
A list is a different kind of data structure from an array. 列表是一种不同于数组的数据结构。
The biggest difference is in the idea of direct access Vs sequential access. Arrays allow both; direct and sequential access, while lists allow only sequential access. And this is because the way that these data structures are stored in memory. 最大的区别在于直接访问和顺序访问的概念。数组允许两个;直接和顺序访问,而列表只允许顺序访问。这是因为这些数据结构存储在内存中的方式。
The structure of the list doesn’t support numeric index like an array is. 列表的结构不像数组那样支持数字索引。
##Linked Lists 链表
It’s a collection of nodes, where each node has a value and a link to the next node in the list.
它是节点的集合,每个节点都有一个值和到列表中下一个节点的链接。
The pointer of the last node points to NULL, or terminator, or a dummy node. 最后一个节点的指针指向NULL,或终止符,或虚拟节点。
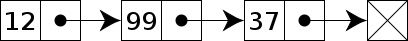 Linked List — wikipedia
链接列表-维基百科
Linked List — wikipedia
链接列表-维基百科
Because of the way it’s built, adding, and removing elements is much, much easier than with an array. 由于它的构建方式,添加和删除元素要比数组简单得多。
But, with arrays, it requires shifting to the left or to the right to keep its meaningful ordered structure. Even adding elements at the end of the array can still require reallocation of the entire array in order to store the array in a contiguous area of memory. 但是,对于数组,它需要向左或向右移动以保持有意义的有序结构。即使在数组末尾添加元素,仍然需要重新分配整个数组,以便将数组存储在连续的内存区域中。
##Doubly Linked List 双向链表
What we have introduced is a linked list, But to be yet a little more specific, this is a called a “Singly Linked List”. We can also have a “Doubly Linked List”. 我们介绍的是一个链表,但更具体一点,这是一个所谓的“单链表”。我们还可以有一个“双链表”。
Instead of each node having a reference just to the next node, we add one more piece of data that it also has a reference to the previous node as well. So, it allows us to go forward and backward, to traverse the list in any direction. 不是每个节点都只有对下一个节点的引用,而是添加另一块数据,它也有对上一个节点的引用。所以,它允许我们前进和后退,以任意方向遍历列表。
 Doubly Linked List — wikipedia
双链表-维基百科
Doubly Linked List — wikipedia
双链表-维基百科
Linked lists in most of the languages are typically implemented as doubly linked lists. 在大多数语言中,>链表通常以双链表的形式实现。
The Singly Vs Doubly Linked List 单链表VS双链表
Adding operation is clearly less work in a singly linked list, because doubly linked list requires changing more links than a singly linked list. 在单链表中添加**操作的工作量显然更少,因为双链表需要比单链表更改更多的链接。
For singly linked list, we assume that we insert at the head or after some given node. 对于单链表,我们假设在头节点或某个给定节点之后插入。
In case of adding before some given node, you need to know the node before that given node, which will require you to sequentially access all the nodes until you find the node you’re looking for. 如果要在某个给定节点之前添加节点,则需要知道该节点之前的节点,这将要求您顺序访问所有节点,直到找到要查找的节点为止。
Removing is simpler and potentially more efficient in doubly linked list, because in singly linked list, you need to know the node before the node to be deleted. 在双链表中,删除**更简单,而且可能更高效,因为在单链表中,您需要知道要删除的节点之前的节点。
##Circular Linked List 循环链表
In a singly linked list, If the next pointer of the last node points back to the first node. Then, it’s “Circular Linked List”. And if the previous pointer of the first node points to the last node as well. Now this would be considered a “Circular Doubly Linked List”. 在单链表中,如果最后一个节点的下一个指针指向第一个节点。然后是“循环链表”。如果第一个节点的前一个指针指向最后一个节点。现在,这将被认为是一个“循环双链表”。
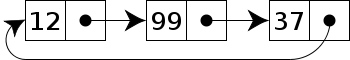
Circular Linked List — wikipedia 圆形链接列表-维基百科
It’s not common, but it can be useful for certain problems. So, if we get to the end of the list and say next, we just start again at the beginning. 这并不常见,但它对某些问题很有用。所以,如果我们到了列表的末尾,说下一个,我们就从开始的地方开始。
##Stacks 栈
Just like the arrays and lists, stacks and queues are also collection of items. They are just different ways we can hold multiple items. It’s last in, first out data structure, with no care about numeric indexes. 正如数组和列表一样,堆栈和队列也是项的集合。它们只是不同的方式,我们可以容纳多个项目。它是最后进入的,先出的数据结构,不关心数值索引。
It’s a collection of items where we add and remove items to and from the top of the stack.
它是一个项集合,我们在堆栈顶部添加和删除项。
 Stack of dirty plates
脏盘子堆
Stack of dirty plates
脏盘子堆
Stack Implementation 栈的实现
A stack can be easily implemented either using an array or a linked list 堆栈可以很容易地通过数组或链表来实现
Usage of Stacks 栈的使用
Stack is not limited to only model the real world situations (same for queues). One of the best uses for a stack in programming is when parsing code or expressions, where you need to do something like validating the correct amount of opening and closing curly braces, square brackets or parenthesis. Stack不仅限于模拟真实世界的情况(队列也是如此)。在编程中,栈的最佳用法之一是解析代码或表达式时,您需要做一些事情,比如验证正确的左大括号、方括号或括号的数量。
The Basic Operations of Stacks 栈的基本操作
They are: push(), pop(), & peek(). push is for pushing a new element on the top of the stack, and pop will return (and remove) the element at the top, while peek will get the element at the top without removing it. 它们是:push()、pop()和peek()。push用于在堆栈顶部推送一个新元素,pop将返回(并删除)顶部的元素,而peek将获得顶部的元素,而不删除它。
Stacks Vs Arrays Vs Linked Lists 栈Vs数组Vs链表
Working with stack is simpler than working with arrays or linked lists, because there is less you can do with a stack. 使用堆栈比使用数组或链表更简单,因为使用堆栈可以做的事情更少。
This is an intentionally limited, an intentionally restricted data structure. All we do is push and pop and maybe peek. And if you’re trying to do anything else with this stack, you’re using the wrong data structure. 这是一个有意限制的数据结构。我们所做的就是推送,弹出,或者偷窥。如果你想用这个堆栈做其他事情,你就用错了数据结构。
##Queues 队列
The key difference between a stack and a queue. Stacks are last in first out (LIFO), while queues are first in first out (FIFO). And as with stacks, we should not even be thinking about numeric indexes. 堆栈和队列之间的关键区别。堆栈是最后的先进先出(LIFO),而队列是第一个先进先出(FIFO)。和堆栈一样,我们甚至不应该考虑数字索引。
It’s a collection of items where we add items to the end and remove items from the front of the queue.
它是项的集合,我们在末尾添加项,并从队列前面删除项。
 Queue of people 排队的人
Queue of people 排队的人
Queue Implementation 队列实现
As with stacks, a queue can be implemented either using an array or a linked list. 与堆栈一样,可以使用数组或链表实现队列。
Usage of Queues 使用队列
Queues are very commonly used in concurrency situations to keep track of what tasks are waiting to be performed and making sure we take them in that order. 队列在并发情况下非常常用,用于跟踪等待执行的任务,并确保按顺序处理它们。
The Basic Operations of Queues 队列的基本操作
Just like a stack: add(), remove(), & peek(). 就像一个堆栈:add(), remove()和peek()。
Priority Queues 优先级队列
Some languages offer a version of a queue, called a priority queue. This allows you to arrange elements in the queue based on their priority. 有些语言提供队列的一个版本,称为优先队列。这允许您根据优先级排列队列中的元素。
It’s a queue, where items with higher priority step ahead of items with lower priority in the queue.
它是一个队列,在队列中优先级较高的项先于优先级较低的项。
How Priority Queues Works 优先队列是如何工作的
When you add items that have the same priority, they will queue as normal in a first in, first out order. If something comes along with a higher priority, then it will go ahead of them in the queue. 当您添加具有相同优先级的项时,它们将按照正常顺序排队。如果有更高优先级的东西出现,那么它将在队列中走在它们前面。
Defining The Priority 定义优先级
You can define based on what an element has higher, lower, or equal priority. This done by implementing a comparator or a compare function (as when sorting arrays), where you provide your own logic for comparing the priority between elements. 您可以根据一个元素的高优先级、低优先级或同等优先级来定义。这可以通过实现一个comparator或一个compare函数(就像对数组进行排序一样)来实现,您可以在比较元素之间的优先级时提供自己的逻辑。
##Deque 双端队列
The deque, pronounced “DEK”, is used when we want to leverage the power of the queue and the stack, where you can add or remove from start or end. deque的发音是“DEK”,当我们希望利用队列和堆栈的功能时,可以使用deque,在这里可以从开始或结束添加或删除。
It’s a queue and a stack at the same time.
它同时是一个队列和一个堆栈。
##Associative Arrays 关联数组
They give the ability to use meaningful keys to work with elements in our data structures, rather than working with numeric indexes as keys. This gives a meaningful relationship between the key and the value. 它们允许使用有意义的键来处理数据结构中的元素,而不是将数字索引作为键。这提供了键和值之间有意义的关系。
It is a collection of key-value pairs.
它是键-值对的集合。
var user = {
firstName: "Bob",
lastName: "Jones",
age: 26,
email: "bob.jones@example.com"
};
The implementation of associative arrays have different names. In Objective-C and Python, they’re called dictionaries. 关联数组的实现有不同的名称。在Objective-C和Python中,它们被称为字典。
The Order of Elements 元素的顺序
Unlike a basic array, In an associative array the keys do not need to be in any specific order. Because order is not a concern in associative arrays. 与基本数组不同,关联数组中的键不需要以任何特定顺序排列。因为顺序与关联数组无关。
Sure, you might find it useful to sort them by key. You might find it useful to sort them by value, or, you might not need to sort it at all. 当然,您可能会发现按键排序很有用。您可能会发现按值对它们进行排序很有用,或者根本不需要对它们进行排序。
Key Duplicates 键重复
The same way that you don’t get the same index number appearing twice in a basic array, there can be no duplicate keys, and keys must be unique in an associative array. 同样地,在基本数组中不会出现两次相同的索引号,不能有重复的键,键在关联数组中必须是唯一的。
Keys & Values Data Types 键&值数据类型
You can usually use any data type as either the key or the value. It is common to use a string as a key. 您通常可以使用任何数据类型作为键或值。通常使用字符串作为键。
Most associate arrays, whether they are called dictionaries or maps or hashes, are implemented using hash table data structure. So, we’ll start by hashing and then dive into hash tables. 大多数关联数组都是使用哈希表数据结构实现的,不管它们是字典、映射还是散列。那么,我们将从哈希开始,然后深入讨论哈希表。
##Hashing 哈希
Hashing is a valuable concept in programming. It’s used, not just in data structures, but in security, cryptography, graphics, audio. 哈希是编程中一个很有价值的概念。它不仅用于数据结构,还用于安全、加密、图形和音频。
It’s a way to take our data and run it through a function, which will return a small, simplified reference generated from that original data.
这是一种获取数据并通过函数运行数据的方法,函数将返回从原始数据生成的一个小的、简化的引用。
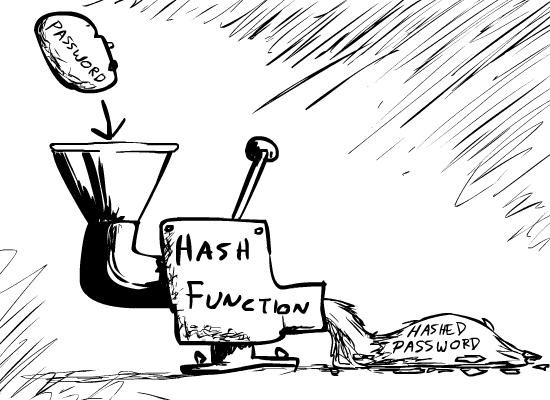 Hashing is commonly used with passwords 哈希通常与密码一起使用
Hashing is commonly used with passwords 哈希通常与密码一起使用
The reference might just be an integer, or letters and numbers, …etc. 引用可能只是一个整数,或者字母和数字,等等。
Why Using Hashing? 为什么使用散列?
Because being able to take a complex object, and hash it down to a single integer representation. So, we can use that integer value to get to a certain location in the data structure. 因为可以把一个复杂的对象,哈希到一个整数表示。因此,我们可以使用这个整数值来到达数据结构中的某个位置。
Hashing Is Not Encryption 散列不是加密
Hash functions are not reversible; They are one way. So, you cannot convert a hash value result back to the original data. Therefore, you lose information when hashing, that’s okay, that’s intentional. 哈希函数是不可逆的;它们是单向的。因此,您不能将哈希值结果转换回原始数据。因此,在哈希过程中会丢失信息,这是故意的。
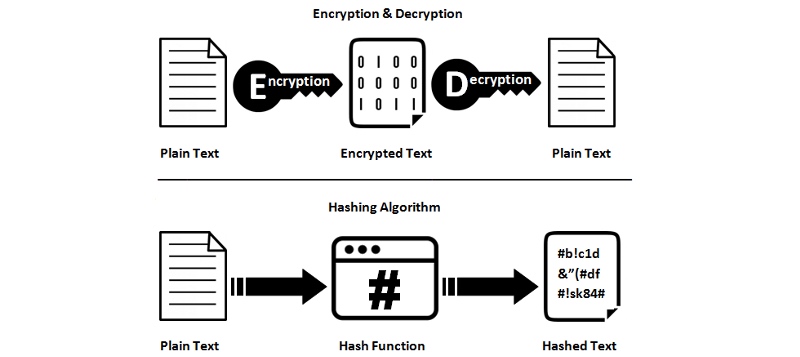 Hashing Vs Encryption — ssl2buy.com 哈希Vs加密- ssl2buy.com
Hashing Vs Encryption — ssl2buy.com 哈希Vs加密- ssl2buy.com
Hashing Function Implementation 哈希函数实现
Say we have a person class defined, and we want a hash function defined on this class. The hash function should return a specific single reference (usually an an integer) for a specific person object. This single integer is generated using the data in a person object (firstname, lastname, birth date, …etc). 假设我们定义了一个person类,我们想在这个类上定义一个哈希函数。哈希函数应该为特定的person对象返回一个特定的引用(通常是一个整数)。这个整数是使用person对象中的数据(firstname、lastname、生日等等)生成的。
Hashing Rules 哈希规则
-
If we take the exact same object, with this same data, and feed it into the hash function again, I would expect the same hash result. 如果我们用同样的对象,同样的数据,再把它输入哈希函数,我期望得到相同的哈希结果。
-
If you have two different objects that you consider equal, they should return the same hash value. 如果有两个你认为相等的不同对象,它们应该返回相同的哈希值。
-
While two equal objects should produce the same hash value, two equal hash values does not guarantee they came from equal objects, Why?Because two different objects might, under some circumstances, deliver the same result out of a hash function (See Hashing Collision). 两个相等的对象应该产生相同的哈希值,但是两个相等的哈希值不能保证它们来自相等的对象,为什么?因为在某些情况下,两个不同的对象可能会从哈希函数传递相同的结果(参见哈希冲突)。
Hashing Collision 哈希碰撞
It’s when we have different objects with different data, but giving the same hash value result. 当我们有不同的对象和不同的数据,但是得到相同的哈希值时。
It could be because the hashing function is simple hash function, but it’s also possible even with more complex hash functions. In most cases that’s okay, we can manage the hash collision. 这可能是因为哈希函数是简单的哈希函数,但即使是更复杂的哈希函数也是可能的。在大多数情况下,这是可以的,我们可以管理哈希冲突。
##Hash Tables 哈希表
The idea of hashing was fundamental to understand the hash table data structure. 哈希的思想是理解哈希表数据结构的基础。
It’s a typical data structure to implement an associative arrays; mapping keys to values.
实现关联数组是一种典型的数据结构;将键映射到值。
 Mapping numbers (keys) to boxes 将数字(键)映射到框
Mapping numbers (keys) to boxes 将数字(键)映射到框
Hash Tables Vs Arrays Vs Lined List 哈希表Vs数组Vs列表
The big benefit of hash tables over arrays and over linked lists is they’re very fast, both for looking at whether an item exists or finding a specific item in a hash table, and for inserting and deleting items. 与数组和链表相比,哈希表的最大好处是它们非常快,既可以查看某个项是否存在,也可以在哈希表中查找特定项,还可以插入和删除项。
How Hash Tables Work? 哈希表是如何工作的?
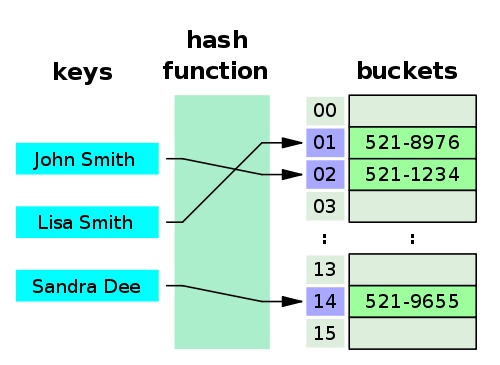 A small phone book as a hash table — wikipedia 一个小电话簿作为哈希表-维基百科
A small phone book as a hash table — wikipedia 一个小电话簿作为哈希表-维基百科
When a hash table is created, it’s really internally a very array-based data structure, and can usually be created with an initial capacity. The hash table consists of an array of slots, or buckets which contain the values. 当创建哈希表时,它实际上是一个非常基于数组的数据结构,通常可以用初始容量创建。哈希表由包含值的槽数组或桶组成。
When adding a key-value pair, It will take our key and it’ll run it through the hash function, getting a specific hash value out (usually an integer). 当添加键-值对时,它会取出我们的键并通过哈希函数运行它,得到一个特定的哈希值(通常是整数)。
If this hash value is large, you might need to simplify it with respect to the current size of the hash table. 如果这个哈希值很大,您可能需要根据哈希表的当前大小对其进行简化。
Then, it will assign the value to an array element with the index equals to the returned hash integer value. 然后,它将把该值赋给一个数组元素,其索引值等于返回的散列整数值。
// adding a key-value pair
hash_table.add(key, value)
// what happen behind the scene
index = hash(key)
index = index % array_size
array[index] = value
Accessing a value given a key follows the same idea. It will take that key, run it through the exact same hash function, and it can then go directly to a specific location that contains the value we’re looking for. 访问给定键的值遵循相同的思想。它会获取那个键,通过完全相同的哈希函数运行它,然后它可以直接进入一个包含我们要查找的值的特定位置。
There’s no linear search, no binary search, no traversing a list. We just go straight to the element we need. 没有线性搜索,没有二进制搜索,没有遍历列表。我们直接得到我们需要的元素。
Managing Collision 管理冲突
We can expect that a hash collision will arise; when we get the same hash value for different keys. But, how to manage it? 我们可以预期哈希碰撞会发生;当我们为不同的键得到相同的哈希值时。但是,如何管理呢?
When we add a new key value pair, and collision happens, It’s going to put that value in the same location, even if there’s another existing value in that location. 当我们添加一个新的键值对,发生碰撞时,它会把那个值放在相同的位置,即使那个位置有另一个现有的值。
Now, hash table implementations have different ways to automatically deal with this. These range from that each location contains a simple collection, like an array, or a linked list. 现在,哈希表实现有不同的方式来自动处理这个问题。每个位置都包含一个简单的集合,比如数组或链表。
So, we would still be able to get to any location very fast, but once we get to the location with multiple values, the hash table will traverse that internal list to find what we’re looking for. 因此,我们仍然能够非常快地到达任何位置,但是一旦我们到达具有多个值的位置,哈希表就会遍历那个内部列表,以找到我们要查找的内容。
Each node in the linked list in turn will contain the value associated with a specific key. In addition, It will contain that key, or a reference to that key. Because in case of multiple values inside the same location, we need to know which key this value belongs to. 链表中的每个节点依次包含与特定键相关联的值。此外,它将包含该键,或对该键的引用。因为对于同一位置内的多个值,我们需要知道这个值属于哪个键。
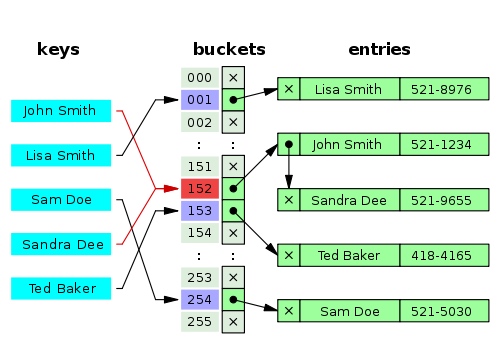 Hash collision resolved by separate chaining — wikipedia 通过单独的链接解决哈希冲突——维基百科
Hash collision resolved by separate chaining — wikipedia 通过单独的链接解决哈希冲突——维基百科
This is what is called the “Separate Chaining Technique” in hash tables. Now, there are other techniques for managing collisions inside hash tables, including open addressing, Cuckoo hashing, hop-scotch, and Robin Hood hashing. 这就是散列表中的“独立链接技术”。现在,还有其他一些管理哈希表内冲突的技术,包括开放寻址、布谷鸟哈希、跳房子和罗宾汉哈希。
Writing Hash Functions 写哈希函数
When you want to store key-value pairs using hash table data structure, It’s probably most of objects already have hash function. The default behavior is usually returns an integer; calculated from the memory address of that object. 当您希望使用哈希表数据结构存储键值对时,可能大多数对象都已经具有哈希函数。默认的行为通常是返回一个整数;从该对象的内存地址计算。
If you ever override the equality behavior in your class, you must override the hash behavior. Because hash codes are so tied to equality, And, if you have two objects that you consider equal, they should return the same hash value. 如果您曾经在类中重写了相等行为,那么您必须重写哈希行为。因为哈希码与相等关系非常紧密,而且,如果有两个你认为相等的对象,它们应该返回相同的哈希值。
Again, If you change what it means for your objects to be equal, you should also change what it means to hash these objects. 同样,如果你改变了对象相等的意义,你也应该改变哈希这些对象的意义。
String objects already overridden their own equality and hashing behavior. So if you have two separate string objects, they will still count as equal, and return the same hash, if they have the same value, even if they’re actually separate string objects allocated in different parts of memory. 字符串对象已经覆盖了它们自己的相等性和散列行为。所以如果你有两个单独的字符串对象,它们仍然是相等的,并且返回相同的散列,如果它们有相同的值,即使它们实际上是分配在内存不同部分的单独的字符串对象。
##Sets 集
When all what you need is a big container you can put a bunch of items into it, where you don’t care about the sequence. 当你只需要一个大容器的时候,你可以把一堆东西放进里面,你不需要考虑顺序。
There is no specific sequence as with a linked list, or a stack, or a queue. There is no key-value pairs as with a hash table. 没有特定的序列,例如链表、堆栈或队列。没有键值对,就像散列表一样。
It’s an unordered collection of items, with no repeated values.
它是一个无序的项目集合,没有重复的值。
By unordered, I mean there is no index like an array. 无序是指没有像数组那样的索引。
 A grocery bag of food 一袋食品
A grocery bag of food 一袋食品
Set Implementation Set实现
Sets are actually use the same idea of hash tables data structure most of the time. But, instead of key-value pairs (hashing a key and store it’s value), when you’re using a set, the key is also considered as the value (or the value is assigned to a dummy or a default value). 集合实际上在大多数情况下都使用哈希表数据结构的相同思想。但是,与键-值对(对键进行哈希并存储其值)不同的是,在使用集合时,键也被认为是值(或将值赋给哑值或默认值)。
So, to get any specific value, or any specific object in the set, you need to have the object itself. And the only reason to do this is to check for it’s existence. This is often referred to as “checking membership”. 所以,要得到集合中的任何特定值,或任何特定对象,你需要对象本身。这样做的唯一原因是为了检验它是否存在。这通常被称为“检查成员资格”。
Sets can be implemented using a self-balancing binary search tree for sorted sets, or a hash table for unsorted sets. 可以使用自平衡二叉搜索树实现排序集,也可以使用散列表实现未排序集。
The Advantage of Sets 集合的好处
Unlike an array, or values in an associative array, or a linked list, sets do not allow duplicates. You cannot add the same object, the same value twice to the same set. 与数组、关联数组中的值或链表中的值不同,集合不允许重复。不能将相同的对象、相同的值两次添加到相同的集合中。
Sets are designed for very fast lookup, to very quickly be able to see if we already have a value contained in a collection. 集合是为快速查找而设计的,以便能够非常快速地查看集合中是否已经包含值。
You can also iterate through all the elements in a set, you just may not have any guaranteed order. 你也可以遍历一个集合中的所有元素,你可能没有任何有保证的顺序。
##Trees 树 The idea of a tree data structure is that we have a collection of nodes, and the nodes have connections, they have links between each other. 树型数据结构的概念是我们有一组节点,这些节点有连接,它们之间有链接。
This sounds similar to linked lists. But in a linked list, we always go from one node to a single specific next node. While in a tree, each node might link to one, or two, or more nodes. 这听起来类似于链表。但是在链表中,我们总是从一个节点到一个特定的下一个节点。在树中,每个节点可能链接到一个、两个或多个节点。
It’s a collection of nodes, where each node might link to one, or two, or more nodes.
它是节点的集合,每个节点可能链接到一个、两个或多个节点。
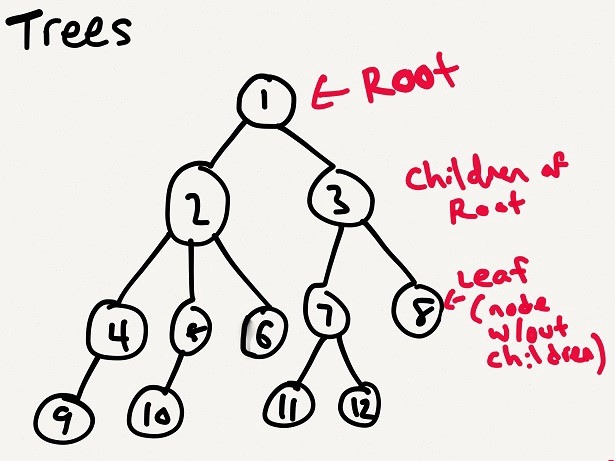 A Tree — richardkho.com
A Tree — richardkho.com
Tree Terminologies 树术语
There are some terminologies that come with the tree. You can find more about them here. They are essential to understand and work with trees. 这棵树附带了一些术语。你可以在这里找到更多关于他们的信息。它们对于理解和研究树木是必不可少的。
Binary Trees 二叉树
A binary tree is just a tree with maximum of two child nodes for any parent node. Binary trees are often used for implementing a wonderfully searchable structure called a “Binary Search Tree” or “BST”. 二叉树就是对于任何父节点最多有两个子节点的树。二叉树通常用于实现一种奇妙的可搜索结构,称为“二叉搜索树”或“BST”。
##Binary Search Trees (BST) 二进制搜索树(BST)
It’s a specific type of binary tree, where the left child node is less than its parent, and a right child node is greater than its parent.
它是一种特定类型的二叉树,其中左子节点小于其父节点,而右子节点大于其父节点。
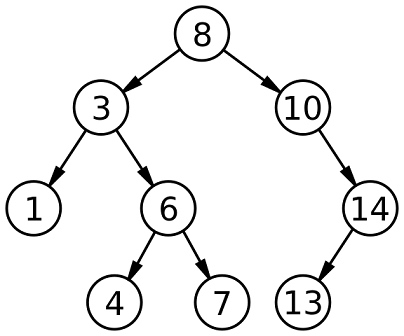 A Binary Search Tree (BST) — wikipedia 一个二叉搜索树(BST) -维基百科
A Binary Search Tree (BST) — wikipedia 一个二叉搜索树(BST) -维基百科
How Binary Search Trees Work? 二叉搜索树是如何工作的?
The the rule is that the left child node must be less than its parents, and a right child node must be greater than its parents, and that rule follows all the way down in the tree. 规则是,左子节点必须小于其父节点,而右子节点必须大于其父节点,这个规则一直延续到树的下面。
And as we insert new nodes with values, the rule will always be followed to make sure that the tree stays sorted. 当我们插入具有值的新节点时,将始终遵循规则以确保树保持排序。
So, It is a data structure that naturally stays sorted and it’s sometimes called “A Sorted Tree” or “An Ordered Tree”. 因此,它是一种自然保持排序的数据结构,有时被称为“排序树”或“有序树”。
Storing Nodes As Key-Value Pairs 将节点存储为键-值对
A binary search trees are often used to store key value pairs, meaning, the nodes consists of a key, and an associated value. And it’s the key that would be used to sort the nodes accordingly in a binary search tree. 二叉搜索树通常用于存储键值对,也就是说,节点由键和关联值组成。这是在二叉搜索树中对节点进行排序的关键。
Duplicates 副本
You can’t have duplicate keys, just as you don’t have duplicate keys in a hash table or even an array. 不能有重复键,就像哈希表甚至数组中不能有重复键一样。
Adding & Accessing Nodes 添加和访问节点
Adding & Accessing nodes follows the same rule mentioned above. If the current node is less than, then go right, if greater than, go left. 添加和访问节点遵循上述相同的规则。如果当前节点小于,则向右,如果大于,则向左。
Retrieve Nodes In Order 按顺序检索节点
The other benefit is binary search trees are staying sorted. So, If we retrieve the items from a left to the right, bottom to top, we will get them all out in order. 另一个好处是二叉搜索树可以保持排序。所以,如果我们从左到右,从下到上检索项目,我们就会按顺序得到它们。
Unbalanced Tree 不平衡的树
It’s when the tree has more levels of nodes on the right hand side than on the left (or vice-versa). 当树的右边的节点比左边的节点多时(反之亦然)。
Although it’s unusual for this kind of thing to happen, but, we can’t always guarantee that the way data is added will allow us to build a tree with a perfectly symmetrical structure all the way down. 虽然这种事情很少发生,但是,我们不能总是保证添加数据的方式能够让我们构建一个结构完全对称的树。
In this case we say that our tree is unbalanced; There are more levels on one side than on the other. And we would have to perform more checks to find or insert or delete any values on the right hand side than we would on the left (or vice-versa). 在这种情况下,我们说树是不平衡的;一边的能级比另一边的能级多。我们需要执行更多的检查来查找、插入或删除右边的任何值,而不是左边的值(反之亦然)。
Binary Search Tree Implementations 二叉搜索树的实现
What we have been talking about is the abstract idea of a binary search tree data structure. But, there are several implementations of this binary search tree idea that are self-balancing binary search trees. 我们一直在讨论的是二进制搜索树数据结构的抽象概念。但是,这个二叉搜索树的思想有几个实现是自平衡的二叉搜索树。
The important idea with balancing a binary search tree is that the number of levels are roughly equal to each other. We don’t have three levels on the left and twenty on the right. 平衡二叉搜索树的重要思想是层的数量大致相等。左边没有三层,右边没有二十层。
Examples of self-balancing trees could be: Red-Black, AVL or Adelson-Velskii and Landis’, Splay, Scapegoat trees, and more. 自我平衡树的例子可以是:红黑树、AVL或Adelson-Velskii和Landis ‘、Splay树、代罪羔羊树等等。
Binary Search Tree Vs Hash Table 二叉搜索树Vs哈希表
Both are fast for insertion, fast for deletion, fast for accessing any element even at large sizes. But, because binary search trees stay sorted, they allow us to get all the items out of the tree in order, where the hash table doesn’t guarantee a specific order. 这两种方法都可以快速插入,快速删除,快速访问任何元素,即使是大的元素。但是,由于二叉搜索树保持排序,它们允许我们按顺序从树中取出所有项,而哈希表不能保证特定的顺序。
##Heaps 堆 Heaps are usually implemented using the idea of a binary tree, not a binary search tree but still, a binary tree. They’re a way of implementing other abstract data types like the priority queue. 堆通常使用二进制树的思想来实现,不是二进制搜索树,而是二进制树。它们是实现其他抽象数据类型(如优先级队列)的一种方法。
It’s a specific type of binary tree, where we add nodes from top to bottom, left to right, and child nodes must be less (or greater) than or equal their parents.
这是一种特定类型的二叉树,我们从上到下、从左到右添加节点,子节点必须小于(或大于)或等于它们的父节点。
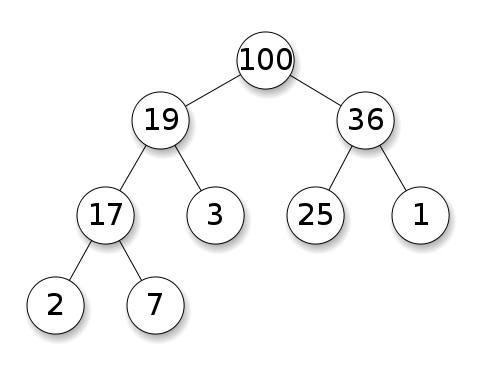 Max Heap — wikipedia 最大堆-维基百科
Max Heap — wikipedia 最大堆-维基百科
Therefore, we completely fill out any level before moving on to the next. So we don’t have to worry about the tree becoming unbalanced like a binary search tree can. 因此,在进入下一个关卡之前,我们将完全填充任何关卡。所以我们不用担心树会像二叉搜索树那样变得不平衡。
Min Vs Max Heap
A min heap states that any child node must be greater than (or equal) its parent node, while a max heap states that any child node must be less than (or equal) its parent node. However, we don’t care if a node is less than or greater than it’s sibling. 最小堆声明任何子节点必须大于(或等于)它的父节点,而最大堆声明任何子节点必须小于(或等于)它的父节点。但是,我们不关心节点是否小于或大于它的兄弟节点。
How Heaps Work? 堆如何工作的呢?
So, In case of Min Heap: 因此,对于最小堆:
- We keep adding elements from top to bottom, left to right 我们一直从上到下,从左到右添加元素
- Then, compare with the parent node; Is it less than its parent? 然后,与父节点进行比较;它比它的父母少吗?
- If so, then swap the node with it’s parent, 如果是,则与它的父节点交换节点,
- Keep doing steps from 2 through 3 until the node is greater than it’s parent (or it becomes the root node). 所示。从2到3一直执行步骤,直到节点大于它的父节点(或者它成为根节点)。
This little swapping of nodes is how a heap keeps itself organized. 这种小的节点交换是堆保持自身组织的方式。
Heap Is Not A Fully Sorted 堆不是完全排序的
Unlike a binary search tree, which does stay sorted, and where we can easily traverse the tree and retrieve everything out in order. 与二叉搜索树不同,二叉搜索树是保持排序的,我们可以轻松地遍历树并按顺序检索所有内容。
Because if you notice, that at any particular level past the root, the values do not have to be in any specific order, just as long as they’re all greater (or less) than their parent. 因为如果您注意到,在根之后的任何特定级别上,值不必以任何特定的顺序出现,只要它们都大于(或小于)它们的父级即可。
One of the benefits of this is a heap does not have to do as much reorganization of itself as may be necessary with a binary search tree. 这样做的好处之一是,堆不必像使用二叉搜索树那样进行大量的自我重组。
The one thing we can be sure about, is that the parent node will always be less or greater than it’s child nodes, and hence the minimum or the maximum value will be always at the top. 我们可以确定的一件事是,父节点总是小于或大于它的子节点,因此最小值或最大值总是在顶部。
And, therefore, heaps are most useful for the idea of a priority queue. 因此,堆对于优先级队列的概念最有用。
##Graphs 图
The limitations of a tree are no longer exist here. A node can link to multiple other nodes, no specific sequence, no root node. 树的局限性不再存在。一个节点可以链接到多个其他节点,没有特定的顺序,没有根节点。
It’s a collection of nodes, where a node can link to multiple other nodes, no specific sequence, no root node. 它是一个节点集合,其中一个节点可以链接到多个其他节点,没有特定的序列,没有根节点。
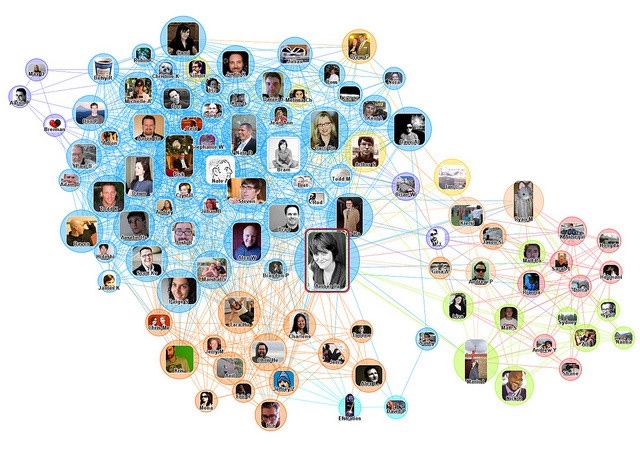 A graph of a social network
社交网络的图表
A graph of a social network
社交网络的图表
Graph Theory In Mathematics 数学中的图论
Because graphs in computer science are so closely linked to graph theory in mathematics. It is common to hear mathematical terms used. So, In graph theory, we call the nodes “vertices”, and the links between them are referred to as “edges”. 因为计算机科学中的图形与数学中的图形理论是紧密联系在一起的。使用数学术语是很常见的。因此,在图论中,我们称节点为“顶点”,它们之间的链接称为“边”。
Graphs Usage 图使用
We could use a graph to model a social network with each node a person. Or, modeling the distances between cities. We could model a ethernet network in an office, or in an entire building, or a city. 我们可以使用一个图形来为每个人的节点建立一个社交网络模型。或者,为城市之间的距离建模。我们可以在办公室、整栋大楼或一座城市建立以太网络模型。
Direct & Undirect Graphs 直接和非直接图
We can also say whether those edges should have a direction to them or not. 我们也可以说这些边是否应该有一个方向。
In some situations, it makes sense that any edge, any connection between two vertices, is only one-way; So, node A is connected to node B, while the reverse is not true; node B is NOT connect to node A. 在某些情况下,任何边,两个顶点之间的任何连接,都是单向的;因此,节点A连接到节点B,反之则不成立;节点B没有连接到节点A。
In other situations, you might want to be able to follow that edge, that link, in either direction; So, node A is connected to node B, and also node B is connected to node A. 在其他情况下,你可能想沿着这条边,这条连杆,在任意方向;节点A连接到节点B,节点B也连接到节点A。
Weighted Graphs 加权图
You can also give every edge a weight; associating a number, with each of the edges. 你也可以给每条边一个权重;将一个数与每条边联系起来。
You could do this to represent, say, the distances between cities, if you were trying to calculate the shortest route between multiple locations. Or, you could use a weight to indicate which edges take priority over other edges. 你可以这样表示,比如说,城市之间的距离,如果你想计算多个地点之间最短的路线。或者,您可以使用权重来指示哪些边优先于其他边。
##Abstract Data Types (ADTs) 抽象数据类型(adt)
Before diving into the abstract data types, what they are, and the difference between them and other concepts. Let’s define what’s meant by a data type. 在深入研究抽象数据类型之前,先了解它们是什么,以及它们与其他概念之间的区别。让我们定义数据类型的含义。
Data Type 数据类型
A variable’s data type determines the values it may contain, plus the operations that may be performed on it.变量的数据类型决定了它可能包含的值,以及可能对其执行的操作。
Data Types consists of: Primitive, Complex or Composite, and Abstract Data Types. 数据类型包括:基本数据类型、复杂数据类型或复合数据类型以及抽象数据类型。
An Abstract Data Type (ADT) 抽象数据类型(ADT)
It’s a data type, just like integers and booleans primitive data types. An ADT consist not only of operations, but also of values of the underlying data and of constraints on the operations. 它是一种数据类型,就像整数和布尔基本数据类型一样。ADT不仅包含操作,还包含底层数据的值和操作上的约束。
A constrains for a stack would be that each pop always returns the most recently pushed item that has not been popped yet. 堆栈的约束条件是,每次弹出总是返回尚未弹出的最近推送的项目。
The actual implementation for an ADT is abstracted away, and we don’t have to care about. So, how a stack is actually implemented is not that important. A stack could be and often is implemented behind the scenes using a dynamic array, but it could be implemented with a linked list instead. It really doesn’t matter. ADT的实际实现是抽象的,我们不需要关心。所以,堆栈是如何实现的并不重要。堆栈可以而且通常是在后台使用动态数组实现的,但是也可以使用链表实现。这真的不重要。
Lists, stacks, queues, and more are all abstract data types. 列表、堆栈、队列等等都是抽象数据类型。
An Abstract Data Type & Data Structure 抽象数据类型和数据结构
ADT is not an alternative to a data structure, they are different concepts. ADT不是数据结构的替代,它们是不同的概念。
When we say the stack data structure, we refer to how stacks are implemented and arrangement in the memory. But, when we say the stack ADT, we refer to the stack data type which has set of defined operations, the operations constrains, and the possible values. 当我们说到堆栈数据结构时,我们指的是堆栈如何在内存中实现和排列。但是,当我们说堆栈ADT时,我们指的是具有一组已定义操作、操作约束和可能值的堆栈数据类型。
We don’t care about the underlying implementation, same as when using integers, we are abstracted away from how integers are represented in the memory, we are only interested in the operations (add, subtract, …), and the possible values (…, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, …). 我们不关心底层实现,使用整数时一样,我们脱离整数在内存中表示,我们只是感兴趣的操作(加、减、…),和可能的值(…−2−1,0,1,2,……)。
Data structures can implement one or more particular abstract data types (ADT), which specify the operations that can be performed on a data structure. 数据结构可以实现一个或多个特定的抽象数据类型(ADT), ADT指定可以在数据结构上执行的操作。
An Abstract Data Type Is NOT An Abstract Class 抽象数据类型不是抽象类
Both have nothing to do with each other. An abstract class defines only the operations, sometimes with comments that describe the constraints, leaving the actual implementation to the inheriting classes. 两者都与对方无关。抽象类只定义操作,有时还带有描述约束的注释,将实际实现留给继承类。
Although ADTs are often implemented as Interfaces (abstract classes) as in Java. For example, The List interface in Java defines the operations of the List ADT, while the inheriting classes define the actual implementation (data structure). 虽然adt通常作为接口(抽象类)实现,就像在Java中那样。例如,Java中的List接口定义了List ADT的操作,而继承类定义了实际的实现(数据结构)。
But, this is not always the case. For example, Java has a stack class, It is a regular concrete class, but a stack is also an abstract data type, meaning, it represents the idea of having a last in, first out data structure. So, stack is a real concrete class and it’s also an abstract data type. 但情况并非总是如此。例如,Java有一个栈类,它是一个常规的具体类,但是栈也是一个抽象的数据类型,也就是说,它代表了一个后进先出的数据结构。stack是一个具体的类,也是一个抽象的数据类型。
An Abstract Data Types Is A Theoretical Concept 抽象数据类型是一个理论概念
An abstract data type (ADT) is a theoretical concept that’s irrelevant to programming keywords. 抽象数据类型(ADT)是一个与编程关键字无关的理论概念。
So, If we have a stack, we have a last in, first out data structure, that we can push and pop and peek. That’s what we expect a stack to be able to do. Whether a stack is implemented as a concrete class or whatever, It still have the idea of a last in, first out data structure. 所以,如果我们有一个堆栈,我们有一个后进先出的数据结构,我们可以推送,弹出和偷看。这就是我们期望堆栈能够做到的。不管堆栈是作为具体类实现的,还是其他什么,它仍然具有后进先出的数据结构的概念。
##Conclusion 结论
Deciding on The Data Structure 决定数据结构
There are some key questions you need to ask before deciding on the data structure 在决定数据结构之前,您需要问一些关键问题
- How much data do you have? 你有多少数据?
- How often does it change?它多久改变一次?
- Do you need to sort it, do you need to search it? Faster to Access, Insert, or Delete?你需要排序吗,你需要搜索吗?更快地访问、插入或删除?
If any place where you only have trivial amounts of data, it isn’t going to matter very much. Unless of course, those amounts of data change so frequently, or you have large amounts of data. 如果任何地方只有少量的数据,那就没有什么关系了。当然,除非这些数据量变化非常频繁,或者您有大量的数据。
Immutable Data Structures 不可变的数据结构
Now, a general principle that immutable or fixed size data structures tend to be faster and smaller in memory than mutable ones. 现在,一个普遍的原则是,不可变或固定大小的数据结构在内存中往往比可变的结构更快更小。
Why should we restrict the features of arrays? The reason is, that the more constraints you have (like fixed size, specific data type, …), the faster and smaller your data structure is able to be. 为什么要限制数组的特性?原因是,约束越多(比如固定大小、特定数据类型……),数据结构就越快越小。
The pitfalls of having a data structure with many features (non-restricted) is the compiler cannot allocate the ideal amount of space, therefore, it must introduce overhead to support the flexibility of the data structure (like different data types, …). 具有许多特性(不受限制的)的数据结构的缺陷是编译器不能分配理想数量的空间,因此,它必须引入开销来支持数据结构的灵活性(比如不同的数据类型,…)。
Improve Your Code Performance 提高代码性能
If you’re looking at existing code to see what to improve on, then see whatever holds the most data. There is no better way to really get the most out of these data structures than when you see some of the performance improvements you can get, just from simply changing from one structure to another. 如果您正在查看现有代码,以查看需要改进的地方,那么请查看保存最多数据的地方。当您看到可以通过简单地从一种结构更改到另一种结构来获得一些性能改进时,没有更好的方法可以真正最大限度地利用这些数据结构。
Differences In Languages 语言的差异
The algorithms used with each data structure differs from one language to another, and the actual implementation of the data structure differs from one language to another. So, It’s worth to look closely at your language documentation. 每种数据结构使用的算法因语言而异,数据结构的实际实现因语言而异。因此,有必要仔细查看您的语言文档。