利用Runtime拦截已经存在的方法大家应该都很熟悉了, 本文主要介绍一些注意点和细节问题。 Runtime Method Swizzling
Objective-C Runtime Method Swizzling 实践
1.直接上代码
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
//交换的是实例方法
Class class = [self class];
SEL originalSelector = @selector(originMethod);//originMethod 已经存在的方法
SEL swizzleSelector = @selector(swizzleMethod);//swizzleMethod 新添加的方法
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
BOOL success = class_addMethod(class, originalSelector, method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
if (success) {
class_replaceMethod(class, swizzledSelector, method_getImplementation(originalMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
});
}
上面的交换的实例方法,交换类方法该怎么写呢?
- Class class = [self class]; 换为 Class class = object_getClass((id)self); 注意是object_getClass,不是objc_getClass
- 上面的class_getInstanceMethod改为class_getClassMethod方法,其他不变,注意Class class = [self class];和class_getInstanceMethod对应;Class class = object_getClass((id)self)和class_getClassMethod对应
代码分析
方法交换写完了,不知道你有没有一下疑问:
1. 为什么上面的为什么写在+ (void)load ,只能写在load吗?
+(void)load 这个方法比较特别,这个方法只要启动APP就会调用,不管你启动有没有没有用到这个类,都会调用这个方法;这个方法是当类或分类被添加到 Objective-C runtime 时被调用的,重载这个方法可以让我们完成一下初始化的操作,这个方法只会调用一次,在这个方法中千万不要进行耗时的操作,比如文件的读写。笔者当年就范过这个错误,导致APP启动变慢。这个方法是在main()方法执行前就执行了。
另外 +load 方法还有一个和其他方法不同的地方,那就是子类、父类和分类中的 +load 方法的实现是被区别对待的。当一个类和它的分类都实现了 +load 方法时,两个方法都会被调用。 以上特别决定了Method Swizzling写在+load 方法比较合适。
2. 子类重写父类的load方法,为什么不调用[super load]?
上面已经说了,子类、父类和分类中的 +load 方法的实现是被区别对待的,系统会自动调用分别调用子类和父类中的+load 方法,所以子类一定不能使用[super load]
3. Method Swizzling 为什么要加 dispatch_once
加dispatch_once就是防止多次调用,确保代码只被执行一次,上面都说了+load 方法在类加载的时候会被 runtime 自动调用一次,而且只调用一次,为什么还加dispatch_once?为了防止程序员的手动调用。
4. 为什么要调用class_addMethod,直接交换(如下)不就行了吗?
SEL originalSelector = @selector(originMethod);//originMethod 已经存在的方法
SEL swizzleSelector = @selector(swizzleMethod);//swizzleMethod 新添加的方法
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
要回到这个问题首首先说一下class_addMethod这个方法的做作用, class_addMethod就是给类添加新的方法,如果类本身已经存在这个方法,就会添加失败返回NO,这里的类本身的方法,意思是不包括从父类继承过来的方法,什么意思?比如father 类有一个eat方法,son类继承自father类,但是son类没有重写父类(也就是father类)的eat方法,那么 son 类使用class_addMethod添加eat方法,就能添加成功,返回YES。
那么问题来了,首先我们要使用Method Swizzling,肯定是因为当前类已经存在了这个方法,如果类不存在这个方法直接使用category添加方法就行了, 当前类已经存在了这个方法,有两种情况:
a 对类本身存在方法直接交换方法
这里的类本身存在方法是指不是从父类继承过来的,这时直接交换即可,如下图,没有问题:


b 对从父类继承过来的方法直接交换方法
交换之后如下图:
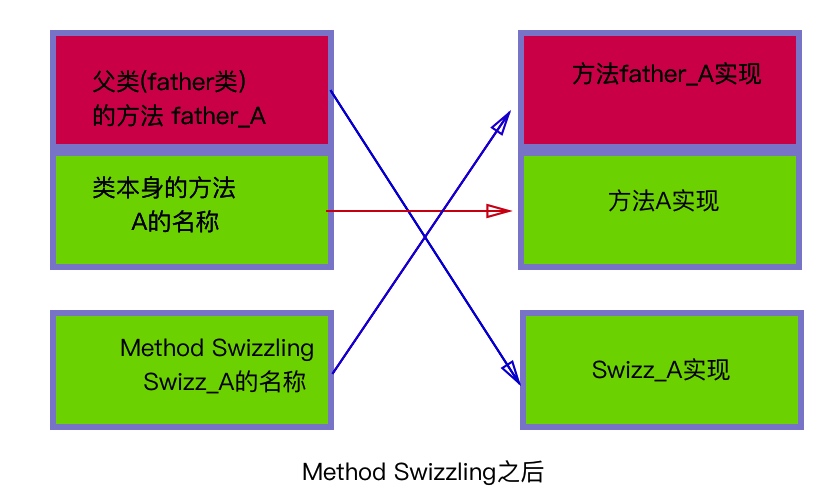 发现问题了吗?父类方法指向了子类的实现,如果用father 类调用father_A方法就会闪退。
实验
发现问题了吗?父类方法指向了子类的实现,如果用father 类调用father_A方法就会闪退。
实验
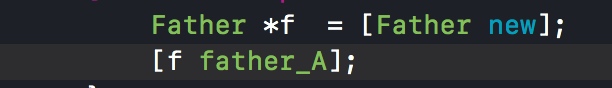

Class aClass = [self class];
SEL originalSel = @selector(father_A);
SEL swizzleSel = @selector(Swizz_A);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, originalSel);
Method swizzleMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, swizzleSel);
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzleMethod);
Father *f = [Father new];
[f father_A];
2018-04-05 16:35:19.732717+0800 runtime 之Method Swizzling[65557:2828735] -[Father Swizz_A]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x1006348f0
2018-04-05 16:35:19.733565+0800 runtime 之Method Swizzling[65557:2828735] *** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '-[Father Swizz_A]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x1006348f0'
c 如果先把父类的方法,利用class_addMethod添加到子类呢,也就是子类重写父类的方法,添加之后如下:
 ,
没看明白是吗?让我们来分析一下添加的代码
,
没看明白是吗?让我们来分析一下添加的代码
class_addMethod(class, originalSelector,method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod),method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod))。
这里一共四个参数,这里的originalSelector就是father_A,method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod)就是Swizz_A的实现。这下明白了吧。
测试
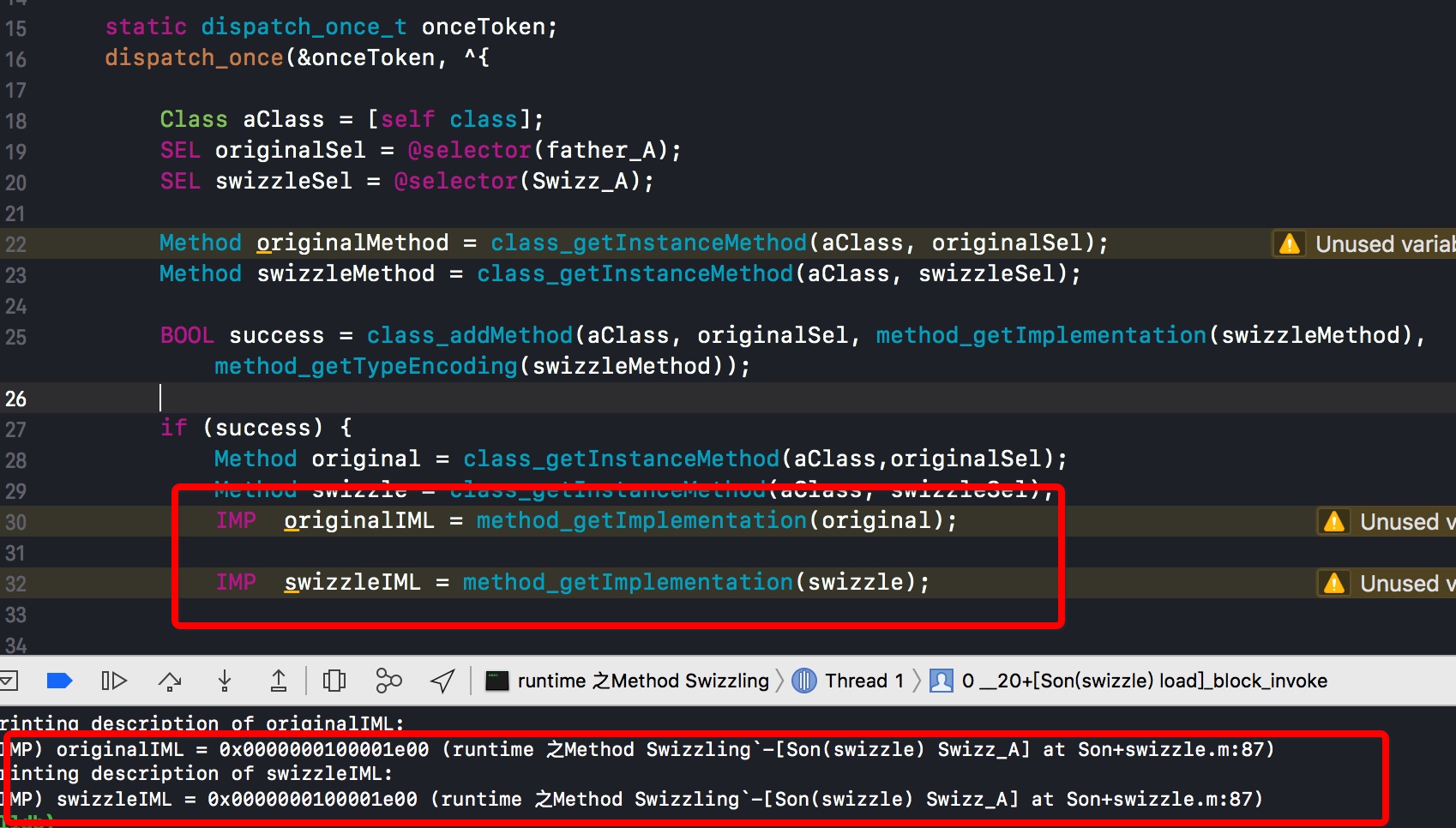
Class aClass = [self class];
SEL originalSel = @selector(father_A);
SEL swizzleSel = @selector(Swizz_A);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, originalSel);
Method swizzleMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, swizzleSel);
BOOL success = class_addMethod(aClass, originalSel, method_getImplementation(swizzleMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzleMethod));
if (success) {
Method original = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass,originalSel);
Method swizzle = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, swizzleSel);
IMP originalIML = method_getImplementation(original);
IMP swizzleIML = method_getImplementation(swizzle);
可以看到originalIML和swizzleIML指向的是同一个实现
d 添加之后为什么不用method_exchangeImplementations方法呢?
通过上图可以看到由于father_A和Swizz_A指向的是同一个实现,所以交换也没有意义,
e 这里为什么还要调用class_replaceMethod方法
好像不调也可以,子类的father_A方法已经指向了Swizz_A,子类调用father_A,相当于调用Swizz_A,也就[son father_A]等同于[son Swizz_A];
在Swizz_A方法调用[super father_A],这个确实可以,就是写法和上面的写法不一样了,上面是
-(void)Swizz_A{
[self father_A];
NSLog(@"son分类里的Swizz_A");
}
-(void)Swizz_A{
[super father_A];
NSLog(@"son分类里的Swizz_A");
}
如果你能确定你要交换的方法是在父类实现的,也可以这么写。
f 调用class_replaceMethod方法,发生了什么呢?
如下图;
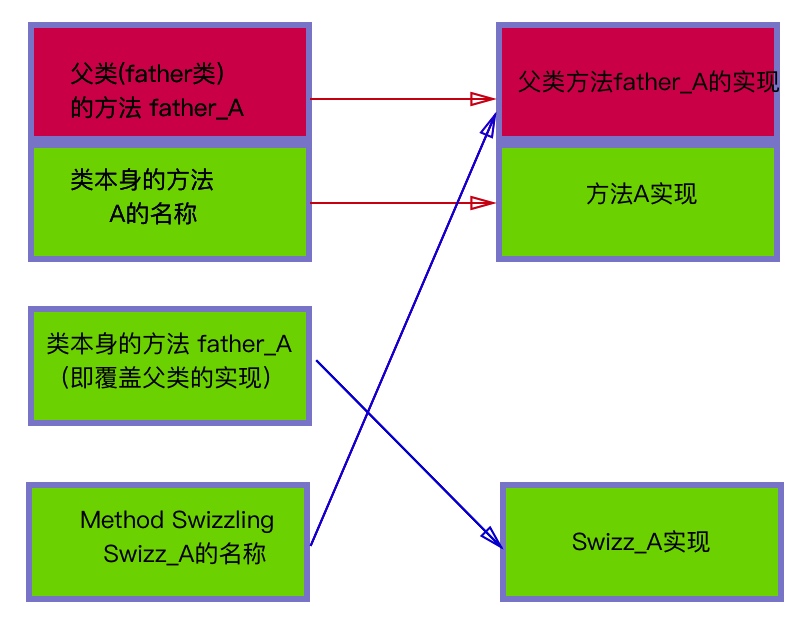
看到了吧,Swizz_A方法名指向了父类的father_A实现,为什么?
class_replaceMethod(class,swizzledSelector,method_getImplementation(originalMethod),method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod))
这里的swizzledSelector就是Swizz_A,method_getImplementation(originalMethod)就是父类的father_A的实现。
上图不对?让我们实验一下
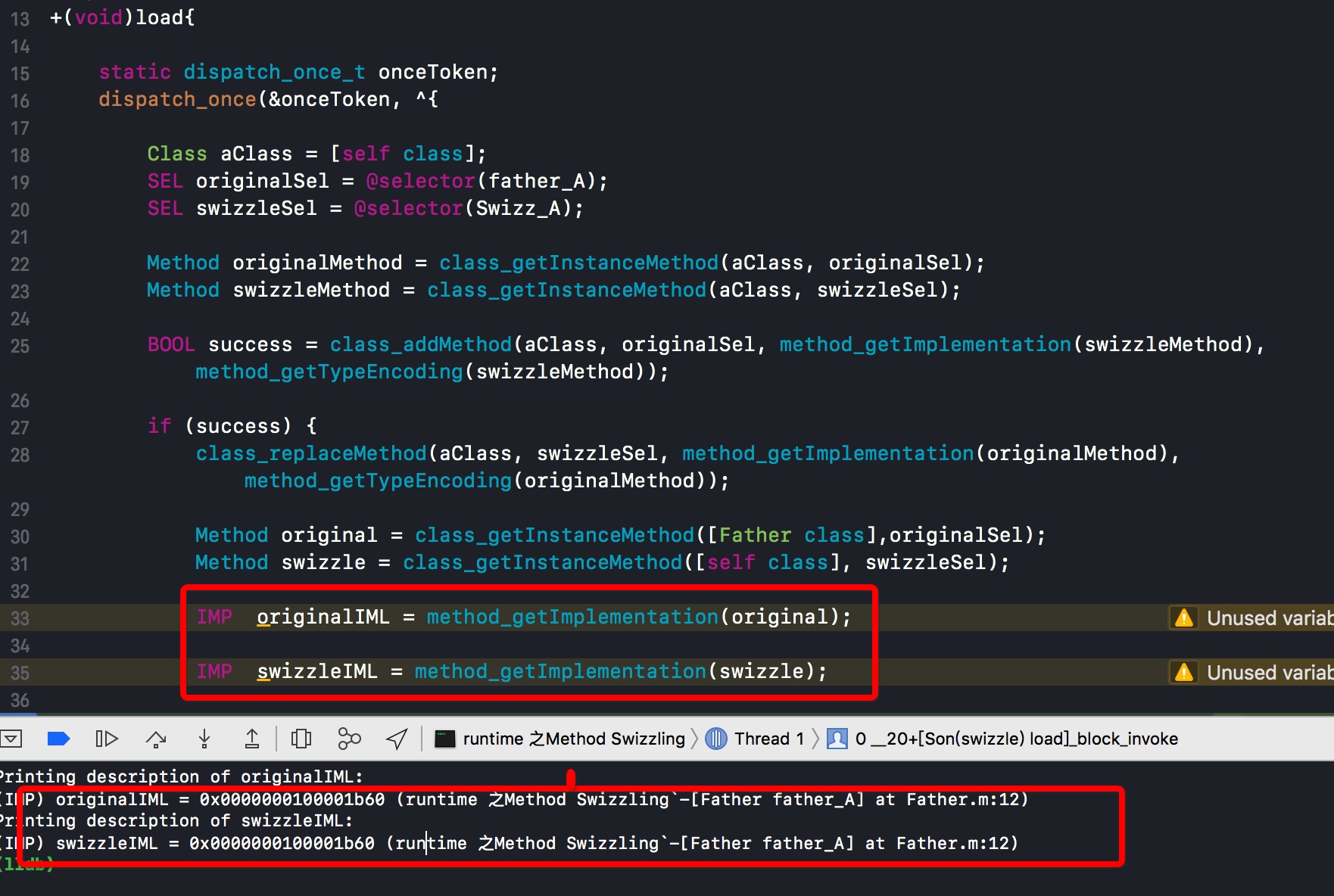 可以看大指向的是同一个IMP
可以看大指向的是同一个IMP
总结:判断class_addMethod这种写法是比较安全的写法,如果你确定要交换的方法存在当前类中,可以直接交换。